Sidney Nolan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sir Sidney Robert Nolan (22 April 191728 November 1992) was one of Australia's leading artists of the 20th century. Working in a wide variety of mediums, his oeuvre is among the most diverse and prolific in all of
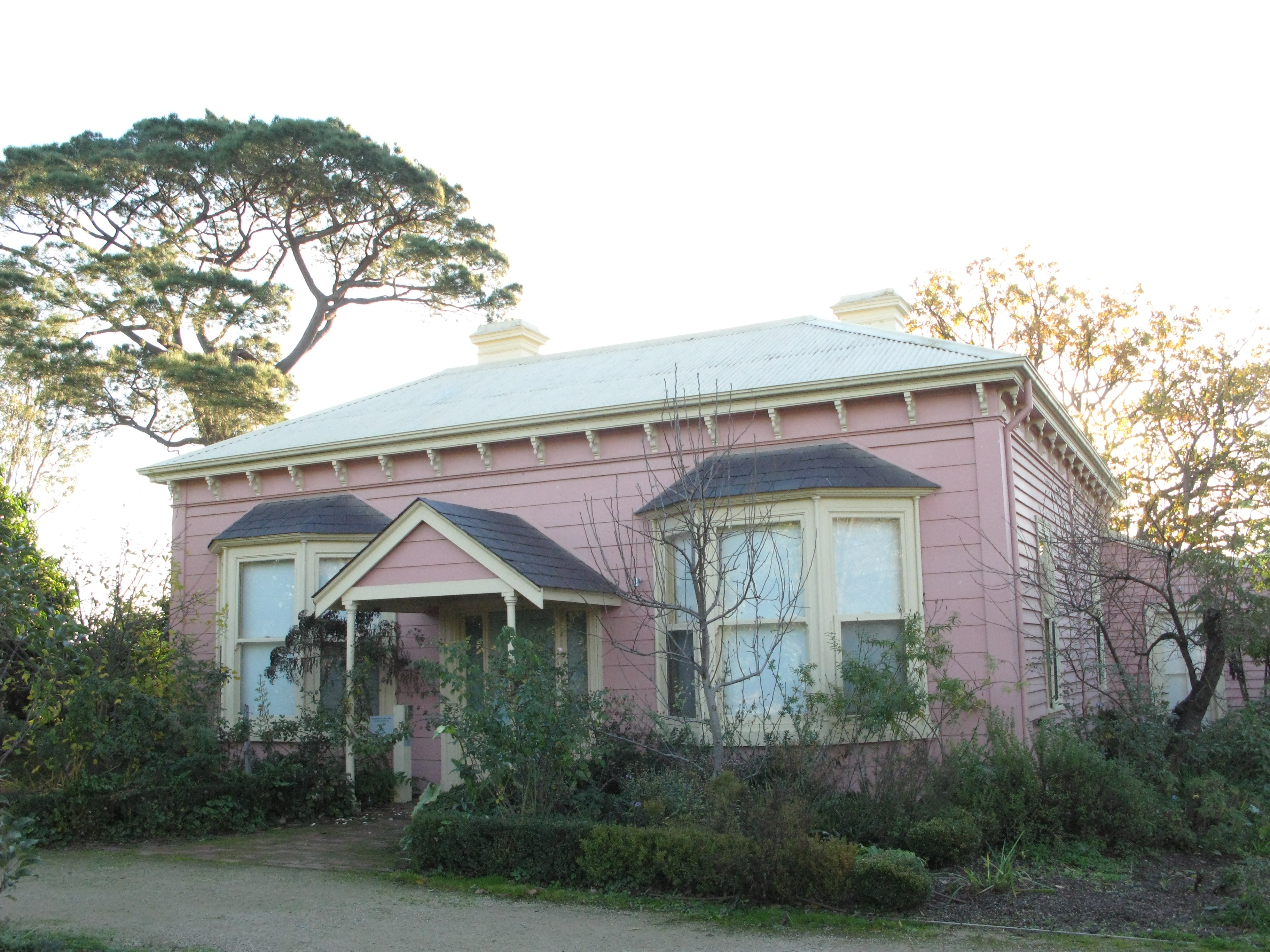 Nolan was a close friend of the arts patrons
Nolan was a close friend of the arts patrons
 Nolan never relied upon one style or technique, but rather experimented throughout his lifetime with many different methods of application, and also devised some of his own. Nolan was inspired by children's art and modernist painting of the early 20th century. During this time many younger artists were veering towards
Nolan never relied upon one style or technique, but rather experimented throughout his lifetime with many different methods of application, and also devised some of his own. Nolan was inspired by children's art and modernist painting of the early 20th century. During this time many younger artists were veering towards 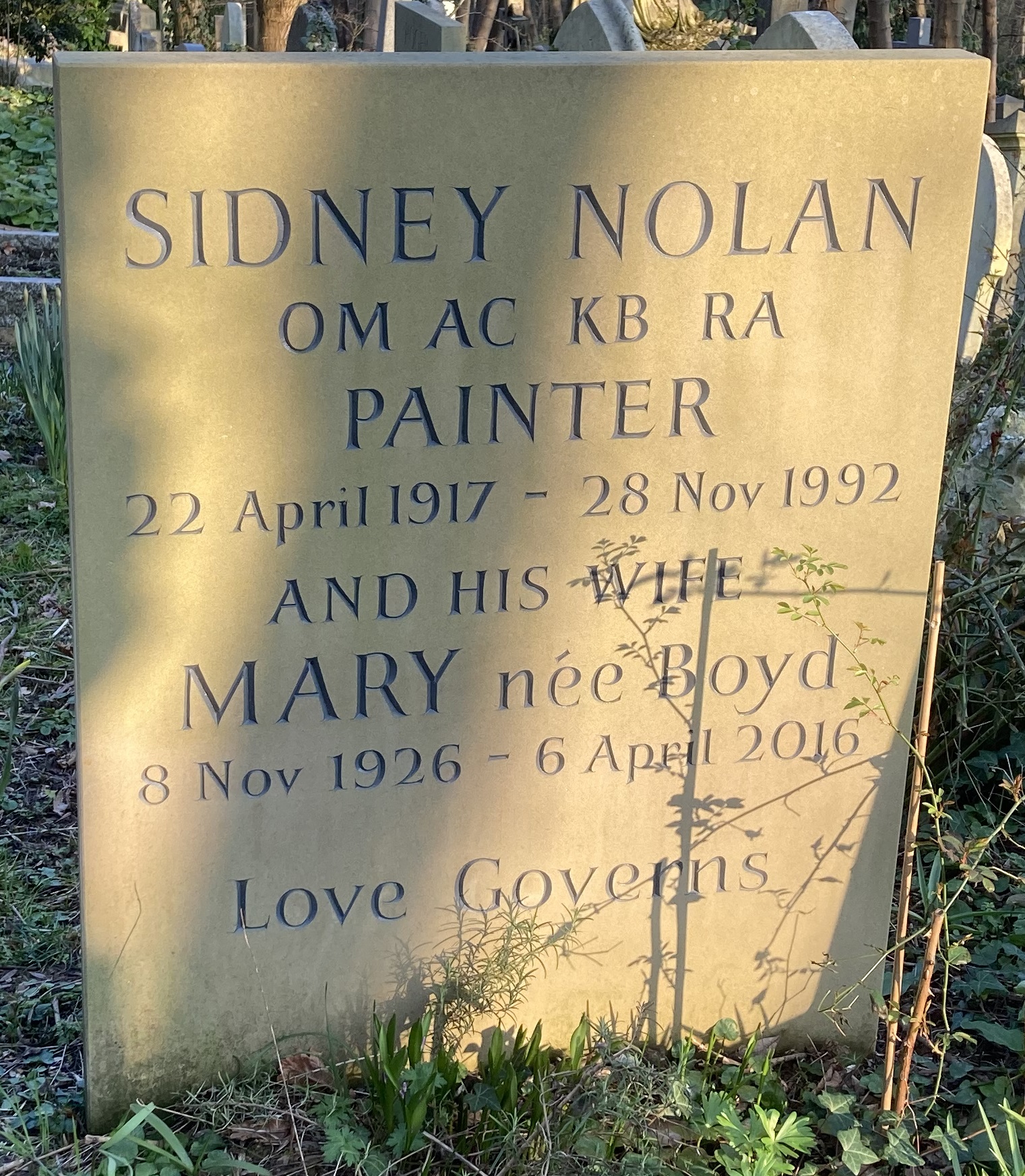 In 1951, Nolan moved to London, England.''The Sidney Nolan Trust''. The Rodd,
In 1951, Nolan moved to London, England.''The Sidney Nolan Trust''. The Rodd,
www.sidneynolantrust.org
/ref> He travelled in Europe, spending a year in 1956 painting themes based on

Sidney Nolan Trust
chaired by Lord Lipsey, was established in 1985 to support artists and musicians, and provide exhibition space for works by Nolan and others at The Rodd, north of
 During the Tin Symphony segment of the
During the Tin Symphony segment of the
The Nolan Collection at Canberra Museum and Gallery
The Sidney Nolan Trust at The Rodd
Sidney Nolan
at the
Sidney Nolan on Artabase
Sidney Nolan on Picture AustraliaSidney Nolan on aCOMMENT
* * *
Sidney Nolan Selected Works
{{DEFAULTSORT:Nolan, Sidney 1917 births 1992 deaths Heide Circle Australian printmakers 20th-century Australian painters 20th-century British male artists Australian expatriates in the United Kingdom Burials at Highgate Cemetery Artists from Melbourne Swinburne University of Technology alumni Royal Academicians Australian Knights Bachelor Australian members of the Order of Merit Companions of the Order of Australia Australian contemporary artists 20th-century British printmakers Australian male painters People from Carlton, Victoria National Gallery of Victoria Art School alumni People from St Kilda, Victoria
modern art
Modern art includes artistic work produced during the period extending roughly from the 1860s to the 1970s, and denotes the styles and philosophies of the art produced during that era. The term is usually associated with art in which the tradi ...
. He is best known for his series of paintings on legends from Australian history
The history of Australia is the story of the land and peoples of the continent of Australia.
Aboriginal Australians, People first arrived on the Australian mainland by sea from Maritime Southeast Asia between 50,000 and 65,000 years ago, and ...
, most famously Ned Kelly
Edward Kelly (December 1854 – 11 November 1880) was an Australian bushranger, outlaw, gang leader and convicted police-murderer. One of the last bushrangers, he is known for wearing a suit of bulletproof armour during his final shootout wi ...
, the bushranger and outlaw
An outlaw, in its original and legal meaning, is a person declared as outside the protection of the law. In pre-modern societies, all legal protection was withdrawn from the criminal, so that anyone was legally empowered to persecute or kill them ...
. Nolan's stylised depiction of Kelly's armour has become an icon of Australian art.
Biography
Early life
Sidney Nolan was born inCarlton
Carlton may refer to:
People
* Carlton (name), a list of those with the given name or surname
* Carlton (singer), English soul singer Carlton McCarthy
* Carlton, a pen name used by Joseph Caldwell (1773–1835), American educator, Presbyterian ...
, at that time an inner working-class
The working class (or labouring class) comprises those engaged in manual-labour occupations or industrial work, who are remunerated via waged or salaried contracts. Working-class occupations (see also " Designation of workers by collar colou ...
suburb of Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a met ...
, on 22 April 1917. He was the eldest of four children. His parents, Sidney (a tram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are ...
driver) and Dora, were both fifth generation Australians of Irish descent. Nolan later moved with his family to the bayside suburb of St Kilda. He attended the Brighton Road State School and then Brighton Technical School and left school aged 14. He enrolled at the Prahran
Prahran (), also pronounced colloquially as Pran, is an inner suburb in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 5 km south-east of Melbourne's Central Business District, located within the City of Stonnington local government area. Prahran recorded a po ...
Technical College (now part of Swinburne University
Swinburne University of Technology (often simply called Swinburne) is a public research university based in Melbourne, Australia. It was founded in 1908 as the Eastern Suburbs Technical College by George Swinburne to serve those without access ...
), Department of Design and Crafts, in a course which he had already begun part-time by correspondence. From 1933, at the age of 16, he began almost six years of work for Fayrefield Hats, Abbotsford, producing advertising and display stands with spray paints and dyes. From 1934 he attended night classes sporadically at the National Gallery of Victoria Art School.
Years at Heide (1941–1947)
John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
and Sunday Reed
Sunday Reed (born Lelda Sunday Baillieu) (15 October 190515 December 1981) was an Australian patron of the arts. Along with her husband, Reed established what is now the Heide Museum of Modern Art.
Personal life
Reed was born on 15 October 1905 ...
, and is regarded as one of the leading figures of the so-called "Heide Circle
The Heide Circle was a loose grouping of Australian artists who lived and worked at "Heide", a former dairy farm on the Yarra River floodplain at Bulleen, a suburb of Melbourne, counting amongst their number many of Australia's best-known modernis ...
" that also included Albert Tucker, Joy Hester
Joy St Clair Hester (21 August 1920 – 4 December 1960) was an Australian artist. She was a member of the Angry Penguins movement and the Heide Circle who played an integral role in the development of Australian Modernism. Hester is best known ...
, Arthur Boyd
Arthur Merric Bloomfield Boyd (24 July 1920 – 24 April 1999) was a leading Australian painter of the middle to late 20th century. Boyd's work ranges from impressionist renderings of Australian landscape to starkly expressionist figuration, ...
and John Perceval
John de Burgh Perceval AO (1 February 1923 – 15 October 2000) was a well-known Australian artist. Perceval was the last surviving member of a group known as the Angry Penguins who redefined Australian art in the 1940s. Other members include ...
. Boyd and Perceval were members of the Boyd artistic family who were centered at "Open Country", Murrumbeena
Murrumbeena is a suburb in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 13 km south-east of Melbourne's Central Business District, located within the City of Glen Eira local government area. Murrumbeena recorded a population of 9,996 at the 2021 cen ...
.
In 1938, he met and married his first wife, graphic designer Elizabeth Paterson, with whom he had a daughter, but his marriage soon broke up because of his increasing involvement with the Reeds. He joined the Angry Penguins
''Angry Penguins'' was an art and literary journal founded in 1940 by surrealist poet Max Harris, at the age of 18. Originally based in Adelaide, the journal moved to Melbourne in 1942 once Harris joined the Heide Circle, a group of avant-garde ...
in the 1940s, after deserting from the army during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
; indeed he was an editor of the ''Angry Penguins'' magazine and painted the cover for the Ern Malley
The Ern Malley hoax, also called the Ern Malley affair, is Australia's most famous literary hoax. Its name derives from Ernest Lalor "Ern" Malley, a fictitious poet whose biography and body of work were created in one day in 1943 by conservat ...
edition published in June 1944. The Ern Malley hoax poems were seen by Nolan and Sunday Reed as being uncannily prescient in touching on their own personal circumstances.Rainey, David. ''Ern Malley: The Hoax and Beyond''. Melbourne: Heide Museum of Modern Art
The Heide Museum of Modern Art, also known as Heide, is an art museum in Bulleen, a suburb of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Established in 1981, the museum houses modern and contemporary art across three distinct exhibition buildings and is s ...
, 2009. , pp. 58-63. Nolan later recalled how he and Sunday felt they 'had a very intimate relationship with the poems', observing that Petit Testament 'was very much to do with our own lives. . . the poetry was tragic. . . and as it turned out our own lives did have a tragic outcome. ..’ The Malley poems remained a real presence to him throughout his life. He painted and drew literally hundreds of Malley-themed works and in 1975 said it inspired him to paint his first Ned Kelly series: "It made me take the risk of putting against the Australian bush an utterly strange object."
He lived for some time at the Reeds' home, "Heide" outside Melbourne (now the Heide Museum of Modern Art
The Heide Museum of Modern Art, also known as Heide, is an art museum in Bulleen, a suburb of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Established in 1981, the museum houses modern and contemporary art across three distinct exhibition buildings and is s ...
). Here he painted the first of his famous, iconic "Ned Kelly" series, reportedly with input from Sunday Reed. Nolan also conducted an open affair with Sunday Reed but subsequently married John Reed's sister, Cynthia
Cynthia is a feminine given name of Greek origin: , , "from Mount Cynthus" on Delos island. The name has been in use in the Anglosphere since the 1600s. There are various spellings for this name, and it can be abbreviated to Cindy, Cyndi, Cyndy, ...
in 1948 after Sunday refused to leave her husband. He had lived in a ménage à trois with the Reeds for several years and after his marriage he continued to see them and visited Heide at least once during their lifetimes. The years there together have been seen as a dominating factor in the subsequent lives of them all.
In November 1976, Cynthia Nolan ended her life by taking an overdose of sleeping pills in a London hotel. In 1978, Nolan married Mary née Boyd (1926–2016), youngest daughter within the Boyd family and previously married to John Perceval
John de Burgh Perceval AO (1 February 1923 – 15 October 2000) was a well-known Australian artist. Perceval was the last surviving member of a group known as the Angry Penguins who redefined Australian art in the 1940s. Other members include ...
.
Career
Nolan painted a wide range of personal interpretations of historical and legendary figures, including explorersBurke and Wills
The Burke and Wills expedition was organised by the Royal Society of Victoria in Australia in 1860–61. It consisted of 19 men led by Robert O'Hara Burke and William John Wills, with the objective of crossing Australia from Melbourne in the ...
, and Eliza Fraser
Eliza Anne Fraser (c.1798 – 1858) was a Scottish woman who was aboard a ship that wrecked at an island off the coast of Queensland, Australia, on 22 May 1836, and who claimed she was taken in by the Bidjara language, Badtjala (Butchella) people ...
. With time his paintings of Mrs Fraser came to be associated with his growing animus towards Sunday Reed. However, when first painted he was still on good terms with the Reeds and sent them photos of the works for their approval. Indeed, he gave one Fraser Island painting to Sunday Reed as a Christmas gift that year.
Probably his most famous work is a series of stylised descriptions of the bushranger Ned Kelly
Edward Kelly (December 1854 – 11 November 1880) was an Australian bushranger, outlaw, gang leader and convicted police-murderer. One of the last bushrangers, he is known for wearing a suit of bulletproof armour during his final shootout wi ...
in the Australian bush
"The bush" is a term mostly used in the English vernacular of Australia and New Zealand where it is largely synonymous with ''wikt:backwoods, backwoods'' or ''hinterland'', referring to a natural undeveloped area. The fauna and flora containe ...
. Nolan left the famous 1946–47 series of 27 Ned Kellys at "Heide", when he left it in emotionally charged circumstances. Although he once wrote to Sunday Reed to tell her to take what she wanted, he subsequently demanded all his works back. Sunday Reed returned 284 other paintings and drawings to Nolan, but she refused to give up the 25 remaining Kellys, partly because she saw the works as fundamental to the proposed Heide Museum of Modern Art and also, possibly, because she collaborated with Nolan on the paintings. Eventually, she gave them to the National Gallery of Australia
The National Gallery of Australia (NGA), formerly the Australian National Gallery, is the national art museum of Australia as well as one of the largest art museums in Australia, holding more than 166,000 works of art. Located in Canberra in th ...
in 1977 and this resolved the dispute. Nolan's ''Ned Kelly'' series follow the main sequence of the Kelly story. However Nolan did not intend the series to be an authentic depiction of these events. Rather, these episodes/series became the setting for the artist's meditations upon universal themes of injustice, love and betrayal. The Kelly saga was also a way for Nolan to paint the Australian landscape in new ways, with the story giving meaning to the place.
Although the Depression and World War II happened during this period, Nolan decided to concentrate on something other than people struggling in life. Nolan wanted to create and define episodes in Australian nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a in-group and out-group, group of peo ...
, to retell the story of a hero
A hero (feminine: heroine) is a real person or a main fictional character who, in the face of danger, combats adversity through feats of ingenuity, courage, or Physical strength, strength. Like other formerly gender-specific terms (like ...
. A hero which now has become a metaphor for humankind—the fighter, the victim, and the hero—resisting tyranny with a passion for freedom. Nolan recognised that the conceptual image of the black square (Kelly's helmet and armour) had been part of modern art since World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. Nolan just placed a pair of eyes into Kelly's helmet which animates its formal shape. As in most of the series, Kelly's steel head guard dominates the composition. Nolan also concentrates on the Australian outback and shows a different landscape in nearly every painting. Nolan's paintings give the audience an insight into the history of Australia but also show others from the world how beautiful Australia is. The intensity of the colours of the land and bush along with its overall smooth texture help create harmony between legend, symbol and visual impact. Kelly is in the centre of the painting but the colours around him help make him stand out. It's a very simplistic picture but highlights that Ned Kelly is an Australian icon.
 Nolan never relied upon one style or technique, but rather experimented throughout his lifetime with many different methods of application, and also devised some of his own. Nolan was inspired by children's art and modernist painting of the early 20th century. During this time many younger artists were veering towards
Nolan never relied upon one style or technique, but rather experimented throughout his lifetime with many different methods of application, and also devised some of his own. Nolan was inspired by children's art and modernist painting of the early 20th century. During this time many younger artists were veering towards abstraction
Abstraction in its main sense is a conceptual process wherein general rules and concepts are derived from the usage and classification of specific examples, literal ("real" or "concrete") signifiers, first principles, or other methods.
"An abstr ...
, Nolan remained committed to the figurative potential of painting. In terms of art history Nolan rediscovered the Australian landscape (Australia has not been an easy country to paint). His love of literature
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to include ...
is seen as visually evident in his work. Other key influences were the modernist
Modernism is both a philosophical and arts movement that arose from broad transformations in Western society during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The movement reflected a desire for the creation of new forms of art, philosophy, an ...
artists such as Paul Cézanne
Paul Cézanne ( , , ; ; 19 January 1839 – 22 October 1906) was a French artist and Post-Impressionism, Post-Impressionist painter whose work laid the foundations of the transition from the 19th-century conception of artistic endeavour to a ...
, Pablo Picasso
Pablo Ruiz Picasso (25 October 1881 – 8 April 1973) was a Spanish painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramicist and Scenic design, theatre designer who spent most of his adult life in France. One of the most influential artists of the 20th ce ...
, Henri Matisse
Henri Émile Benoît Matisse (; 31 December 1869 – 3 November 1954) was a French visual artist, known for both his use of colour and his fluid and original draughtsmanship. He was a draughtsman, printmaker, and sculptor, but is known prima ...
and Henri Rousseau
Henri Julien Félix Rousseau (; 21 May 1844 – 2 September 1910)
at the Danila Vassilieff Danila Vassilieff (22 March 1958) was a Russian-born Australian painter and sculptor. He has been called the "father of Australian modernism". Life Danila Ivanovich Vassilieff (Данила Иванович Васильев) was born in 1897 ...
in at the Danila Vassilieff Danila Vassilieff (22 March 1958) was a Russian-born Australian painter and sculptor. He has been called the "father of Australian modernism". Life Danila Ivanovich Vassilieff (Данила Иванович Васильев) was born in 1897 ...
Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a met ...
, with his simple and direct art, was significant for Nolan.
In his series, Kelly is a metaphor for Nolan himself. Nolan, like the bushranger, was a fugitive from the law. In July 1944, facing the possibility that he would be sent to Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i ...
on front-line duty, Nolan went absent without leave. He adopted the alias Robin Murray, a name suggested by Sunday Reed, whose affectionate nickname for him was "Robin Redbreast". So when he created this series he viewed himself as the misunderstood hero/artist like the protagonist, Kelly. "Nolan like this Kelly figure has also been a hero, a victim, a man who armoured himself against Australia and who faced it, conquered it, lost it…. ambiguity personified."
Nolan's Ned Kelly series is one of the greatest sequences of Australian paintings of the 20th century. His simplified depiction of Kelly in his armour has become an iconic Australian image. In 1949, when the series was exhibited at the Musée National d'Art Moderne
The Musée National d'Art Moderne (; "National Museum of Modern Art") is the national museum for modern art of France. It is located in Paris and is housed in the Centre Pompidou in the 4th arrondissement of the city. In 2021 it ranked 10th in ...
in Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
, the museum's director Jean Cassou
Jean Cassou (9 July 1897 – 15 January 1986) was a French writer, art critic, poet, member of the French Resistance during World War II and the first Director of the Musée national d'Art moderne in Paris.
Biography
Jean Cassou was born at Bi ...
called the works "a striking contribution to modern art" and that Nolan "creates in us a wonder of something new being born". Works from Nolan's second Kelly series (ca. mid-1950s) were acquired by major international galleries, including the Museum of Modern Art
The Museum of Modern Art (MoMA) is an art museum located in Midtown Manhattan, New York City, on 53rd Street between Fifth and Sixth Avenues.
It plays a major role in developing and collecting modern art, and is often identified as one of ...
in New York and the Tate Modern
Tate Modern is an art gallery located in London. It houses the United Kingdom's national collection of international modern and contemporary art, and forms part of the Tate group together with Tate Britain, Tate Liverpool and Tate St Ives. It is ...
in London. English critic Robert Melville wrote in 1963 that Nolan's Kelly belonged to "the company of twentieth-century personages which includes Picasso
Pablo Ruiz Picasso (25 October 1881 – 8 April 1973) was a Spanish painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramicist and Scenic design, theatre designer who spent most of his adult life in France. One of the most influential artists of the 20th ce ...
's minotaur, Chirico's mannequins, Ernst
Ernst is both a surname and a given name, the German, Dutch, and Scandinavian form of Ernest. Notable people with the name include:
Surname
* Adolf Ernst (1832–1899) German botanist known by the author abbreviation "Ernst"
* Anton Ernst (1975-) ...
's birdmen, Bacon's popes and Giacometti
Alberto Giacometti (, , ; 10 October 1901 – 11 January 1966) was a Swiss sculptor, painter, Drafter, draftsman and Printmaking, printmaker. Beginning in 1922, he lived and worked mainly in Paris but regularly visited his hometown Borgonovo, ...
's walking man".
Paintings of Dimboola
Dimboola is a town in the Shire of Hindmarsh in the Wimmera region of western Victoria, Australia, 334 kilometres north-west of Melbourne.
History
Situated on the Wimmera River, Dimboola was previously known as 'Nine Creeks'. Following a surve ...
landscapes by Sidney Nolan, who was stationed in the area while on army duty in World War II, can be found in the National Gallery of Victoria
The National Gallery of Victoria, popularly known as the NGV, is an art museum in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Founded in 1861, it is Australia's oldest and most visited art museum.
The NGV houses an encyclopedic art collection across two ...
.
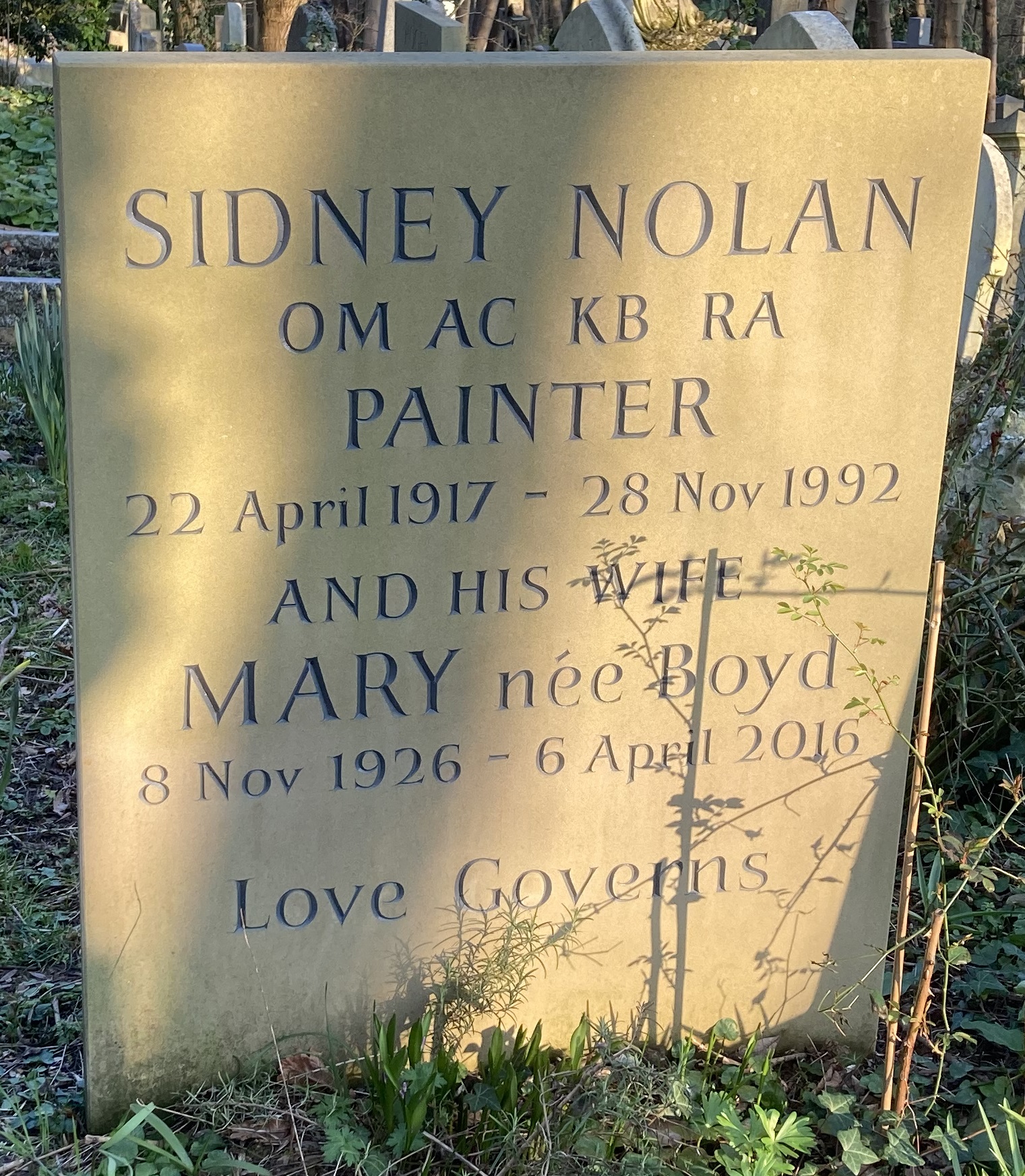 In 1951, Nolan moved to London, England.''The Sidney Nolan Trust''. The Rodd,
In 1951, Nolan moved to London, England.''The Sidney Nolan Trust''. The Rodd, Presteigne
Presteigne (; cy, Llanandras: the church of St. Andrew) is a town and community in Radnorshire, Powys, Wales on the south bank of the River Lugg. Formerly the county town of the historic county of Radnorshire, the town has, in common with ...
, Herefordshire
Herefordshire () is a county in the West Midlands of England, governed by Herefordshire Council. It is bordered by Shropshire to the north, Worcestershire to the east, Gloucestershire to the south-east, and the Welsh counties of Monmouthshire ...
, England. (Leafletwww.sidneynolantrust.org
/ref> He travelled in Europe, spending a year in 1956 painting themes based on
Greek Mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical co ...
while in Greece. In Paris, he studied engraving
Engraving is the practice of incising a design onto a hard, usually flat surface by cutting grooves into it with a Burin (engraving), burin. The result may be a decorated object in itself, as when silver, gold, steel, or Glass engraving, glass ...
and lithography
Lithography () is a planographic method of printing originally based on the immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone (lithographic limestone) or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by the German a ...
with S. W. Hayter at Studio 17t two years there. He became friends with the poet Robert Lowell
Robert Traill Spence Lowell IV (; March 1, 1917 – September 12, 1977) was an American poet. He was born into a Boston Brahmin family that could trace its origins back to the ''Mayflower''. His family, past and present, were important subjects i ...
and produced illustrations for some of his books. Nolan was a prolific book cover illustrator, his images enhancing the dust jackets of over 70 publications. During this period, Nolan's first London solo exhibition occurred at the Whitechapel Gallery
The Whitechapel Gallery is a public art gallery in Whitechapel on the north side of Whitechapel High Street, in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. The original building, designed by Charles Harrison Townsend, opened in 1901 as one of the fir ...
between June and July 1957.
In 1965, Nolan completed a large mural (20 m by 3.6 m) depicting the 1854 Eureka Stockade
The Eureka Rebellion was a series of events involving gold miners who revolted against the British administration of the colony of Victoria, Australia during the Victorian gold rush. It culminated in the Battle of the Eureka Stockade, which ...
, rendered in enamelled jewellery on 1.5 tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
s of heavy gauge copper. Nolan employed the "finger-and-thumb" drawing technique of Indigenous Australian sandpainters to create the panoramic scene. Commissioned by economist H. C. Coombs, the mural is located at the entrance to the Reserve Bank of Australia
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) is Australia's central bank and banknote issuing authority. It has had this role since 14 January 1960, when the ''Reserve Bank Act 1959'' removed the central banking functions from the Commonwealth Bank.
Th ...
's Melbourne office on Collins Street.
During the period of 1968–1970, Nolan embarked on the creation of a monumental mural entitled ''Paradise Garden''. This project consisted of 1,320 floral designs split into three subsections that were created using crayon and dyes. The intent of the subsections was to show the lifecycles of the plants, starting with the primeval plants emerging from the mud, transitioning to their full burst of colour in springtime, and the completion of the life cycle with the withering plants returning to the earth.
In England, Nolan attended the Aldeburgh Festival
The Aldeburgh Festival of Music and the Arts is an English arts festival devoted mainly to classical music. It takes place each June in the Aldeburgh area of Suffolk, centred on Snape Maltings Concert Hall.
History of the Aldeburgh Festival
Th ...
and was encouraged by the organiser and composer Benjamin Britten
Edward Benjamin Britten, Baron Britten (22 November 1913 – 4 December 1976, aged 63) was an English composer, conductor, and pianist. He was a central figure of 20th-century British music, with a range of works including opera, other ...
to show paintings at the festivals. He continued to travel widely in Europe, Africa, China, Australia, and even Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest contine ...
.
Death
Nolan died in London on 28 November 1992 at the age of 75, he was survived by his wife and two children. He was buried in the Eastern part ofHighgate Cemetery
Highgate Cemetery is a place of burial in north London, England. There are approximately 170,000 people buried in around 53,000 graves across the West and East Cemeteries. Highgate Cemetery is notable both for some of the people buried there as ...
, London.
Work

Stage designs
Nolan's lifelong engagement with the theatre began in 1939 when he was commissioned to create décor for French ballet dancerSerge Lifar
Serge Lifar ( ua, Сергій Михайлович Лифар, ''Serhіy Mуkhailovуch Lуfar'') ( 15 December 1986) was a Ukrainian ballet dancer and choreographer, famous as one of the greatest male ballet dancers of the 20th century. No ...
's revised version of ''Icare''. Lifar, then on tour in Australia with the Original Ballet Russe
The Original Ballet Russe (originally named Ballets Russes de Monte-Carlo) was a ballet company established in 1931 by René Blum and Colonel Wassily de Basil as a successor to the Ballets Russes, founded in 1909 by Sergei Diaghilev. The company ...
, offered Nolan the job after a chance encounter with his abstract work. ''Icare'' premiered on 16 February 1940 at the Theatre Royal in Sydney.
In 1964, Robert Helpmann
Sir Robert Murray Helpmann CBE ( Helpman, 9 April 1909 – 28 September 1986) was an Australian ballet dancer, actor, director, and choreographer. After early work in Australia he moved to Britain in 1932, where he joined the Vic-Wells Ballet (n ...
enlisted Nolan to design the set and costumes for his ballet ''The Display
''The Display'' is an Australian ballet produced and choreographed by Robert Helpmann to music by Malcolm Williamson for The Australian Ballet. Described as the first wholly Australian ballet, ''The Display'' had an all-Australian cast, with sets a ...
''. Set at a bush picnic, the piece relates the mating rituals of the lyrebird
A lyrebird is either of two species of ground-dwelling Australian birds that compose the genus ''Menura'', and the family Menuridae. They are most notable for their impressive ability to mimic natural and artificial sounds from their environme ...
to the masculine posturing of Australian males. Nolan created a series of green-blue gauze panels to evoke the filtered light of the forest. One contemporary critic remarked that Nolan's décor "not merely recreates the haunt of the lyrebird. It is the deep, rich mysterious gloom of a sunlight shafted Australian rainforest with the pillars of its ghostly white gums rising through its depths."
In London, he created the designs for Kenneth MacMillan
Sir Kenneth MacMillan (11 December 192929 October 1992) was a British ballet dancer and choreographer who was artistic director of the Royal Ballet in London between 1970 and 1977, and its principal choreographer from 1977 until his death. Ea ...
's ''The Rite of Spring'' (1962) at the Royal Ballet
The Royal Ballet is a British internationally renowned classical ballet company, based at the Royal Opera House in Covent Garden, London, England. The largest of the five major ballet companies in Great Britain, the Royal Ballet was founded in ...
, and for Saint-Saëns' ''Samson et Dalila'' (1981) and Mozart's ''Die Entführung aus dem Serail'' (1987), directed by Elijah Moshinsky
Elijah Moshinsky (8 January 1946 – 14 January 2021) was an Australian opera director, theatre director and television director who worked for the Royal Opera House, the Metropolitan Opera, the Royal National Theatre, and BBC Television, among ...
at the Royal Opera
The Royal Opera is a British opera company based in central London, resident at the Royal Opera House in Covent Garden. Along with the English National Opera, it is one of the two principal opera companies in London. Founded in 1946 as the Cove ...
. Only ''The Rite of Spring'' remains in the repertory.
Honours and awards
In the 1963 New Year Honours List, Nolan was appointed CBE. In the 1981 Birthday Honours List, Nolan was appointed aKnight Bachelor
The title of Knight Bachelor is the basic rank granted to a man who has been knighted by the monarch but not inducted as a member of one of the organised orders of chivalry; it is a part of the British honours system. Knights Bachelor are the ...
for service to art, despite his war desertion. He received the Order of Merit
The Order of Merit (french: link=no, Ordre du Mérite) is an order of merit for the Commonwealth realms, recognising distinguished service in the armed forces, science, art, literature, or for the promotion of culture. Established in 1902 by K ...
(OM) in 1983. In 1983, Nolan settled in Herefordshire
Herefordshire () is a county in the West Midlands of England, governed by Herefordshire Council. It is bordered by Shropshire to the north, Worcestershire to the east, Gloucestershire to the south-east, and the Welsh counties of Monmouthshire ...
. ThSidney Nolan Trust
chaired by Lord Lipsey, was established in 1985 to support artists and musicians, and provide exhibition space for works by Nolan and others at The Rodd, north of
Kington, Herefordshire
Kington is a market town, electoral ward and civil parish in Herefordshire, England. According to the Parish, the ward had a population of 3,240, while the 2011 Census registered a population of 2,626.
Geography
Kington is from the border w ...
.
He was made a Companion of the Order of Australia
The Order of Australia is an honour that recognises Australian citizens and other persons for outstanding achievement and service. It was established on 14 February 1975 by Elizabeth II, Queen of Australia, on the advice of the Australian Gove ...
(AC) in 1988 having declined being made an Officer in 1975. In 1975, Sir John Kerr, the then Governor-General, wrote to the Queen's then Private Secretary, Sir Martin Charteris, to inform him of Nolan's decision to decline. Kerr indicated in his letter that he thought Nolan should have been offered the rank of Companion instead and that he had intended to convey his view to Sir Garfield Barwick, the inaugural Chair of the Order of Australia Council, but that Barwick had already sent Nolan the letter asking whether Barwick would decline the honour of AO. Kerr speculated to Charteris that, having been made CBE in the 1960s, being made an AO, "...may have seemed to him no great advancement."
He was also elected an honorary member of the American Academy of Arts and Letters
The American Academy of Arts and Letters is a 300-member honor society whose goal is to "foster, assist, and sustain excellence" in American literature, music, and art. Its fixed number membership is elected for lifetime appointments. Its headqu ...
and a member of the Royal Academy of Arts
The Royal Academy of Arts (RA) is an art institution based in Burlington House on Piccadilly in London. Founded in 1768, it has a unique position as an independent, privately funded institution led by eminent artists and architects. Its purpo ...
.
Legacy
 During the Tin Symphony segment of the
During the Tin Symphony segment of the 2000 Summer Olympics opening ceremony
The opening ceremony of the 2000 Summer Olympics took place on the evening of Friday 15 September 2000 in Stadium Australia, Sydney, during which the Games were formally opened by Governor-General Sir William Deane. As mandated by the Olympic C ...
, a multitude of performers donned stylised costumes based on Nolan's distinctive Ned Kelly imagery, and a painting from Nolan's original 1946-47 Ned Kelly series was displayed on a giant screen in the stadium.
In 2010, '' First-class Marksman'' (1946) became the most expensive Australian painting ever sold. Dubbed "the missing Nolan", the painting was the only one in Nolan's first series of 27 Ned Kelly paintings not in the collection of the National Gallery of Australia. It was purchased by the Art Gallery of New South Wales
The Art Gallery of New South Wales (AGNSW), founded as the New South Wales Academy of Art in 1872 and known as the National Art Gallery of New South Wales between 1883 and 1958, is located in The Domain, Sydney, Australia. It is the most importa ...
for $5.4 million.
The cinematography for English film director Nicolas Roeg
Nicolas Jack Roeg (; 15 August 1928 – 23 November 2018) was an English film director and cinematographer, best known for directing '' Performance'' (1970), ''Walkabout'' (1971), ''Don't Look Now'' (1973), ''The Man Who Fell to Earth'' (1976 ...
's 1971 Australian film ''Walkabout
Walkabout is a rite of passage in Australian Aboriginal society, during which males undergo a journey during adolescence, typically ages 10 to 16, and live in the wilderness for a period as long as six months to make the spiritual and traditiona ...
'' was heavily influenced by Nolan. The small boy's hallucination of camel riders in the desert was a direct reference to Nolan's Burke and Wills paintings.
Two of Nolan's paintings, ''The Abandoned Mine'' (1948) and ''Ned Kelly'' (1955) were included in Quintessence Editions Ltd.'s 2007 book ''1001 Paintings You Must See Before You Die''.
Melbourne writer Steven Carroll
Steven Carroll (born 1949) is an Australian novelist. He was born in Melbourne, Victoria and studied at La Trobe University. He has taught English at secondary school level, and drama at RMIT. He has been Drama Critic for ''The Sunday Age'' new ...
's 2011 novel ''Spirit of Progress'' is inspired by ''Woman and Tent'' (1946) by Nolan, who based the painting on Carroll's eccentric great-aunt. The young artist in the novel, Sam, is based on Nolan. Nolan's relationship with Sunday Reed provided the framework for Alex Miller
Alex Miller (born 4 July 1949) is a Scottish football manager and former player. As a player, he had a 15-year career with Rangers, winning several trophies. As a manager, he won the 1991–92 Scottish League Cup with Hibernian. He subsequen ...
's 2011 novel '' Autumn Laing''.
Nolan will be the subject of an upcoming film titled ''When We Were Modern'', directed by Philippe Mora
Philippe Mora (born 1949) is a French Australian film director.
Early life and career
Philippe Mora was born in Paris, France in 1949, and grew up at the centre of the Australian arts scene of the 1950s and began making films with an 8mm camera ...
and starring Clayton Watson
Clayton Watson (born 23 March 1977) is an Australian producer, actor, writer, and director. He grew up in the Australian outback on a sheep station close to Morgan, a small town in South Australia. He is best known for his breakthrough role as Ki ...
. This film had not been made as of July 2014. Mora's film ''Absolutely Modern'' premiered in 2013. Based on 1940s Heide, it tells of Modernism, the female muse and the role of sexuality in Art.
David Rainey's 2014 play "The Ménage at Soria Moria" is a fictitious performance piece exploring the relationship between Nolan and the Reeds – both the heady days at Heide during the 1940s, and the less well known degeneration over the next 35 years.
Several documentary films have been made about Nolan. ''This Dreaming, Spinning Thing'' was commissioned by ABCTV as a companion film to Nolan's 1967 retrospective exhibition at the Art Gallery of New South Wales
The Art Gallery of New South Wales (AGNSW), founded as the New South Wales Academy of Art in 1872 and known as the National Art Gallery of New South Wales between 1883 and 1958, is located in The Domain, Sydney, Australia. It is the most importa ...
. It was made with a script by Australian novelist George Johnston. ''Kelly Country'' (1972), directed by Stuart Cooper
Stuart W. Cooper (born 1942) is an American filmmaker, actor and writer.
Career
Cooper was a resident in the United Kingdom in the 1960s and 1970s where his most notable film appearance was as one of ''The Dirty Dozen'', Roscoe Lever, in 1967. ...
with commentary by Orson Welles
George Orson Welles (May 6, 1915 – October 10, 1985) was an American actor, director, producer, and screenwriter, known for his innovative work in film, radio and theatre. He is considered to be among the greatest and most influential f ...
, explores Australia's landscape and folklore through Nolan's imagery. Nolan's ''Paradise Garden'' poems and drawings are examined in British director Jonathan Gili
Jonathan Gili (19 April 1943 – 1 October 2004) was a film-maker, editor and director, who produced numerous and wide-ranging television documentary and features programmes, mostly for the BBC.
Education
The son of Catalan publisher and translat ...
's 1974 film of the same name. A 2009 documentary by filmmaker Catherine Hunter, ''Mask and Memory'' charts the course of Nolan's personal life, including his complex relationship with the Reeds at Heide. Narrated by Judy Davis
Judith Davis (born 23 April 1955) is an Australian actress in film, television, and on stage. With a career spanning over 40 years, she has been commended for her versatility and regarded as one of the finest actresses of her generation. Frequen ...
, the film concludes that the three main women in Nolan's life, Sunday Reed, Cynthia Nolan and Mary Nolan, played bigger roles in the development of his art than is often discussed.
Among Australian artists, Nolan's estate was identified as the third largest in Australia in 2013, following those of Brett Whiteley
Brett Whiteley AO (7 April 1939 – 15 June 1992) was an Australian artist. He is represented in the collections of all the large Australian galleries, and was twice winner of the Archibald, Wynne and Sulman prizes. He held many exhibitions ...
and Russell Drysdale
Sir George Russell Drysdale (7 February 1912 – 29 June 1981), also known as Tass Drysdale, was an Australian artist. He won the prestigious Wynne Prize for ''Sofala'' in 1947, and represented Australia at the Venice Biennale in 1954. He was i ...
.
See also
* Australian artReferences
Bibliography
* * * Fallowell, Duncan, ''20th Century Characters'', ch. Going Round the Rodd: Sir Sidney and Lady Nolan in Herefordshire, (London, Vintage Books, 1994) * * * * * * * * * *External links
*The Nolan Collection at Canberra Museum and Gallery
The Sidney Nolan Trust at The Rodd
Sidney Nolan
at the
Art Gallery of New South Wales
The Art Gallery of New South Wales (AGNSW), founded as the New South Wales Academy of Art in 1872 and known as the National Art Gallery of New South Wales between 1883 and 1958, is located in The Domain, Sydney, Australia. It is the most importa ...
Sidney Nolan on Artabase
Sidney Nolan on Picture Australia
* * *
Sidney Nolan Selected Works
{{DEFAULTSORT:Nolan, Sidney 1917 births 1992 deaths Heide Circle Australian printmakers 20th-century Australian painters 20th-century British male artists Australian expatriates in the United Kingdom Burials at Highgate Cemetery Artists from Melbourne Swinburne University of Technology alumni Royal Academicians Australian Knights Bachelor Australian members of the Order of Merit Companions of the Order of Australia Australian contemporary artists 20th-century British printmakers Australian male painters People from Carlton, Victoria National Gallery of Victoria Art School alumni People from St Kilda, Victoria